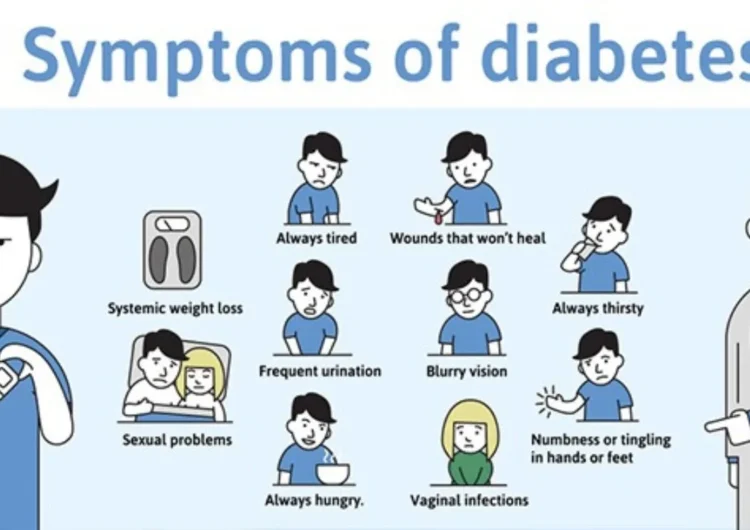
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels. Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, which can help prevent serious complications. Here’s a comprehensive look at the common symptoms associated with diabetes and why they occur.
1. Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
One of the hallmark symptoms of diabetes is frequent urination, known medically as polyuria. High blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb the excess glucose. When they can’t keep up, the excess glucose is excreted in the urine, leading to more frequent urination.
2. Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia)
As a result of frequent urination, the body loses a lot of fluids, leading to dehydration. This dehydration triggers an intense feeling of thirst, known as polydipsia. Drinking more water becomes necessary to compensate for the fluid loss, but it can become a cycle if the blood sugar remains uncontrolled.
3. Extreme Hunger (Polyphagia)
People with diabetes may experience intense hunger or polyphagia. This occurs because the body’s cells aren’t able to absorb glucose for energy due to either a lack of insulin or insulin resistance. As a result, the body feels deprived of energy, leading to increased hunger as it tries to source fuel.
4. Unexplained Weight Loss
Despite eating more, people with untreated diabetes often lose weight. When cells can’t access glucose, the body starts breaking down fat and muscle for energy, leading to weight loss. This symptom is more common in people with type 1 diabetes but can also occur in type 2 diabetes.
5. Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue is a common symptom of diabetes and is caused by the body’s inability to efficiently use glucose for energy. Without adequate insulin or insulin function, glucose stays in the blood instead of entering cells, leaving the body drained of energy.
6. Blurred Vision
High blood sugar levels can cause the lenses of the eyes to swell, leading to blurred vision. If blood sugar levels fluctuate, it can affect your vision temporarily. Left untreated, diabetes can damage blood vessels in the retina, which can lead to more severe eye problems like diabetic retinopathy.
7. Slow-Healing Sores or Frequent Infections
People with diabetes often experience slow wound healing and are more susceptible to infections. High blood sugar levels impair the immune system, slowing down the healing process and increasing the likelihood of infections. This is particularly common with foot sores and skin infections.
8. Numbness or Tingling in Hands and Feet
Nerve damage, or neuropathy, is a common complication of diabetes, especially if blood sugar levels have been elevated for a prolonged period. This can result in sensations like numbness, tingling, or pain in the extremities, particularly in the hands and feet.
9. Dark Patches of Skin (Acanthosis Nigricans)
Acanthosis nigricans is a condition characterized by dark, velvety patches of skin, usually in areas with skin folds such as the neck, armpits, and groin. This is often a sign of insulin resistance and can be an early indication of type 2 diabetes.
10. Mood Changes and Irritability
Fluctuating blood sugar levels can affect mood and mental health. People with diabetes may experience increased irritability, depression, or anxiety, partly due to the impact of blood sugar levels on brain function.